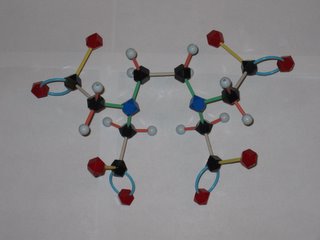
Orac has been posting about the abuse of chelation therapy for treating autism and other disorders. So what's a chelate and how does it work to remove metal ions from the body? EDTA is shorthand for ethylenediamminetetraacetic acid, which has the structure shown at the left. The disodium calcium salt of EDTA is the usual chemotheraputic form. Lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogens and oxygens of the EDTA (tagged blue and red in the photo) latch onto the metal. This Lewis acid-base reaction results in the metal being sequestered inside the EDTA molecule. Tucked away inside the EDTA, the metal can't accumulate in the body's tissues and is eventually eliminated. EDTA has different affinities for different metal ions, but is a pretty effective scavenger of most metal ions, including iron and calcium. Removal of too much calcium can result in cardiac arrest, so EDTA is not without safety isses, as Orac points out!
The word chelation come from the Greek for claw. Molecules that attach to metals at multiple points, like EDTA, are called multidentate ligands from their capacity to "bite" onto the metal. EDTA makes a hexadentate metal-ligand complex (6 points of attachment) with some ions, a pentadentate complex with others.
















Sodium and calcium salts of EDTA are, of course, commonly used food additives.
ReplyDeletehttp://www.access.gpo.gov/nara/cfr/waisidx_04/21cfr172_04.html
I don't know how the daily intake of EDTA from foods compares with therapeutic doses.
Indeed yes, EDTA is also in shampoos....
ReplyDeleteI am curious what the doses are in food...I'll have to check it out!
EDTA's chelating properties make it a popular choice for treating pediatric Pb toxicity. However, as you pointed out, it's lack of specificity between divalent cations has lead drug companies to research alternatives.
ReplyDeleteI remember when I first learned about the meaning of the terms "chelation" and "dentate" back in gen chem. I thought that it was not only "neat" but also so appropriate. This post brought back some of the fun memories of introductory general chemistry for me!
ReplyDeleteSo what is known about why the coordination number can differ?
ReplyDeleteThe CDC is no longer recommending EDTA as the treatment of choice for pediatric lead poisoning...the alternatives are much more selective (and therefore safer).
ReplyDeleteelia, size controls to some extent how many sites the EDTA occupies, also what else might be in solution.
ReplyDelete